Page 1
Loading page ...
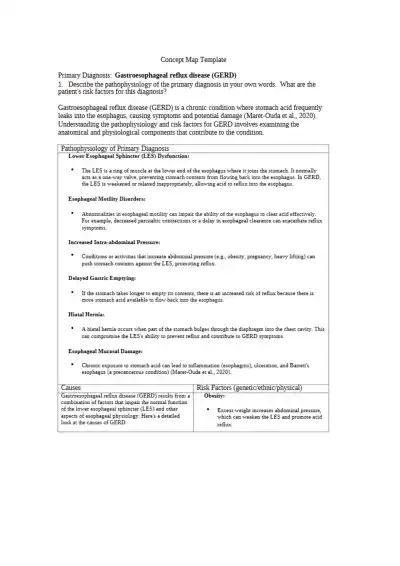
Concept map on GERD pathophysiology: LES dysfunction, impaired esophageal motility, delayed gastric emptying, hiatal hernia, and increased intra-abdominal pressure lead to acid reflux and mucosal damage.

Loading page ...
This document has 11 pages. Sign in to access the full document!